What is power factor? Power factor formula
In the study of electronics engineering, we often hear the term power factor. It plays an important role in understanding the efficiency of electrical circuits. Let us understand power factor in simple language in this blog post and also learn its formula.
What is Power Factor?
In simple words, power factor is the ratio of that part of the total current drawn by an electric circuit that is actually used to do useful work. We express it in percentage (%).
High Power Factor: This is an ideal situation, where most of the current is used to do the actual work. It is considered to be between 90% to 100%. High power factor is an indicator of efficiency, which means less energy is wasted.
Low Power Factor: This means that a large part of the current is being spent in generating reactive power in the circuit instead of doing actual work. This is a power factor of less than 80% and indicates inefficiency, leading to more energy being wasted.
Power Factor Formula
Power Factor (PF) is calculated by the following formula:
PF = Real power (kW) / Apparent power (kVA)
Real power (kW): This is the power used to do actual work in the circuit, which is measured in kilowatts (kW).
Apparent power (kVA): This is the total power that the circuit draws from the supply source, measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA).
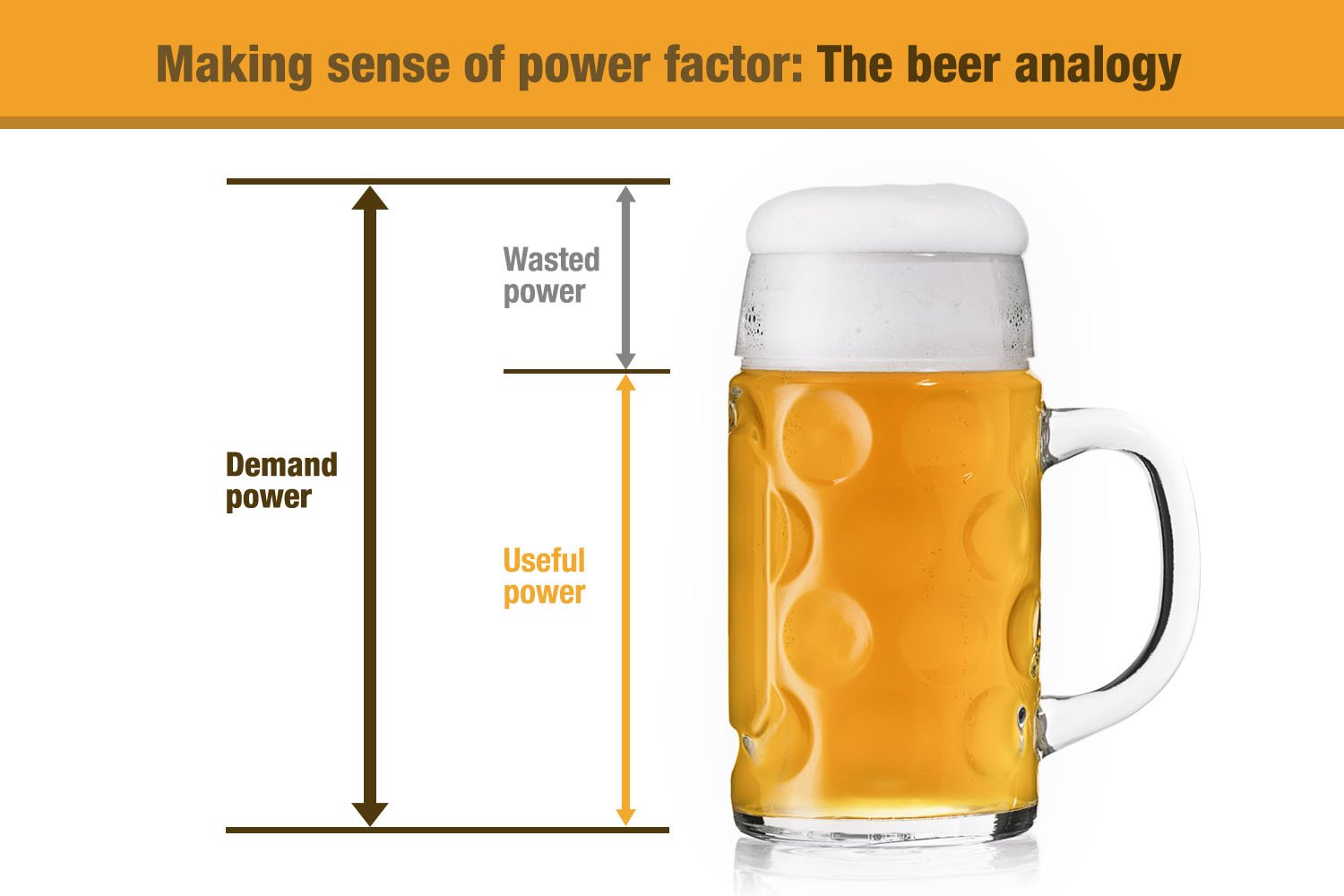
Image Credit: fluke.com
Beer Analogy:
Have you ever noticed that a cold beer becomes less enjoyable when there is too much foam in the glass? To understand power factor, you can imagine a glass of beer.
Total Glass Capacity: This is similar to apparent power (kVA). It shows how much total power the supply source is delivering.
Bee (eer): This is similar to real power (kW). This is the part you can drink and enjoy (the real work).
Foam: This is similar to reactive power. It does not perform any useful function, but rather takes up space in the glass.
For high power factor, you want as much beer as possible in the glass and as little foam as possible. Similarly, for a good power factor, you want the majority of the current drawn by the circuit to be used to do actual work.
Example:
Suppose the current drawn by a motor is 10 amperes (A) and the voltage is 220 volts (V). If the actual power of the motor is 2 kilowatts (kW), what will be its power factor?
Apparent power (kVA) = V x A = 220 V × 10 A = 2200 VA = 2.2 kVA
Power Factor (PF) = 2 kW / 2.2 kVA = 0.91 (approximately 91%)
In this example, the power factor of the motor is 91%, which is a good value and shows that the motor is working efficiently.
Conclusion
Power factor is important in understanding the efficiency of electrical circuits. High power factor ensures energy saving and low electricity bills. In the field of electronics engineering, power factor correction techniques are often used to improve low power factors.
Hope this blog post was helpful to you in understanding power factor and its formula!



.png)
Comments
Post a Comment